Тираннозавр против аллозавра
Содержание:
Примечания
- ↑
- Татаринов Л. П. Очерки по эволюции рептилий. Архозавры и зверообразные. — М. : ГЕОС, 2009. — С. 73. — 377 с. : ил. — (Труды ПИН РАН, Т. 291). — 600 экз. — ISBN 978-5-89118-461-9.
- Бейли Дж., Седдон Т. Доисторический мир / И. Б. Шустова. — М.: Росмэн, 1995. — 100—101, 108, 136 с. — ISBN 5-7519-0097-9.
- Glut, Donald F. Allosaurus // Dinosaurs: The Encyclopedia. — Jefferson, North Carolina : McFarland & Co, 1997. — P. 105—117. — ISBN 978-0-89950-917-4.
- ↑ Paul, Gregory S. Predatory dinosaurs of the world: a complete illustrated guide. — New York : Simon and Schuster, 1988. — ISBN 0-671-61946-2.
- ↑ Bakker, Robert T.: Brontosaur killers: Late Jurassic allosaurids as sabre-tooth cat analogues. Gaia, Vol. 15 (1998); pp. 145—158
- Chure, Daniel J. A new species of Allosaurus from the Morrison Formation of Dinosaur National Monument (Utah–Colorado) and a revision of the theropod family Allosauridae. — Columbia University, 2000.
- Foster, John. 2007. Jurassic West: the Dinosaurs of the Morrison Formation and Their World. Bloomington, Indiana:Indiana University Press. p. 117.
- ↑
- J. H. Madsen. 1976. «Allosaurus fragilis: a revised osteology». Utah Geological and Mineral Survey Bulletin 109: 1—163.
История изучения
Из-за «костяных войн» между Маршем и Коупом в 1880-х годах, возникла путаница в названиях видов и родов. Первые окаменелости были описаны геологом Фердинандом Вандивером Хайденом в 1869 году. Хайдену останки были переданы фермерами из Колорадо, которые нашли их в Формациях Моррисон. Хайден послал образцы Джосефу Лейди, принявшему их за останки уже известного в то время европейского динозавра Poekilopleuron. Впоследствии Лейди решил, что эти останки заслуживают отнесения к отдельному роду — Antrodemus.
Реконструкция голотипа аллозавра, выполненная Чарльзом Р. Найтом
Первые окаменелости типового вида найдены в верхнеюрских отложениях, относящихся к формации Моррисон. Отниел Чарлз Марш описал типовой вид A. fragilis в 1877 году на основании частично сохранившихся трёх позвонков, фрагментов рёбер, зубов, костей ног и плечевой кости. Само название «аллозавр», означающее «странный ящер», было дано из-за того, что его позвонки сильно отличались от позвонков других динозавров, известных в то время. Название типового вида fragilis означает «хрупкий» или «ломкий», было дано из-за хрупкого строения позвонков. Эдвард Коуп и Чарльз Марш, будучи в научной конкуренции, не успевали сравнивать свои новые находки со старыми. Из-за этого некоторые окаменелости, которые сейчас относятся к видам или подвидам аллозавра, были выделены в отдельные роды. К таким псевдородам относятся Creosaurus, Labrosaurus и Epanterias.
После открытия и описания голотипа аллозавр в Колорадо, Марш сконцентрировал работу в Вайоминге, потом, в 1883 году, снова работал в Колорадо, где депутат Флеш нашёл почти полный скелет аллозавра и несколько частичных. В 1879 году один из помощников Коупа нашёл образец в районе Комо Блеф, в Вайоминге, но, видимо, Куоп не смог раскопать эти образцы из-за их огромного количества. После раскопки этих образцов в 1903 году (спустя несколько лет смерти после Коупа), оказалось, что это одни из самых полных останков терапода. Кроме того, в Комо Блеф рядом со скелетом аллозавра найден скелет апатозавра. Также в Комо Блеф были обнаружены останки других тероподов, но они пока ещё не описаны.
Путаница с названиями усугубляется краткостью описаний, оставленных Маршем и Коупом. В 1901 году Сэмюэль Уенделл Уиллистон высказал предположение, что неправильно выделять креозавра и эпантериаса в отдельные от аллозавра рода. В качестве доказательства Уиллистон указал на то, что Марш никогда не был в состоянии отличить аллозавра от креозавра. Самая ранняя попытка разобраться в ситуации была предпринята Чарльзом У. Гилмором в 1920 году. Он пришёл к выводу, что хвостовые позвонки, определённые как принадлежащие Antrodemus, ничем не отличаются от тех же позвонков аллозавра. Таким образом, следует отдавать предпочтение раннему названию, так как они имеют приоритет. С тех пор название Antrodemus употреблялось для названия этого рода более пятидесяти лет, пока Джеймс Мэдсен (James Henry Madsen Jr.) не изучил останки, найденные в Кливленд Ллойде, и не пришёл к выводу, что следует использовать название аллозавр, поскольку Antrodemus был описан на слишком скудном материале.
Останки из Кливленд Ллойда
В Кливленд Ллойде (расположенном вблизи Кливленда, штат Юта, США) был обнаружен так называемый «Карьер динозавров», в котором было найдено 44 скелета аллозавров (Allosaurus fragilis). В юрском периоде на этом месте было болото, в котором увяз гигантский брахиозавр и со временем аллозавры собирались вокруг него для кормления. В результате чего многие из них оказались затянуты в трясину.
В октябре 1965 года Кливленд Ллойд был объявлен национальным природным заповедником.
Paleontology
Allosaurus was one of the largest and most prolific predators of the Late Jurassic, found in North America, Portugal, and Tanzania. The first Allosaurus fossils were found in 1877 by Othniel Marsh, during the ‘Bone Wars’ between Marsh and Edward Drinker Cope. Allosaurus was widespread throughout North America, yet despite its success, its branch from the Allosauridae seems to haven’t evolved any further beyond the Late Jurassic. However, relatives such as Acrocanthosaurus, Carcharodontosaurus and Giganotosaurus continued to thrive into the Cretaceous.
An Allosaurus about to fall asleep.
The bite of Allosaurus wasn’t very strong and instead, it is theorized to use its upper jaw like a hatchet to inflict bleeding damage, although the possibility of this hunting technique is still debated. It is also believed that Allosaurus also used its muscular, clawed arms to grapple onto its prey. Latest publishments has described that some paleontologists suspected this theropod could be an opportunistic cannibal; as allosaurus likely scavenged their own deceased specimens.
Paleoecology
Allosaurus lived in semiarid environments with distinct wet and dry seasons, and flat floodplains alongside dozens of other species of dinosaur, including the sauropods Diplodocus, Apatosaurus, Brachiosaurus and Camarasaurus, other herbivores such as Dryosaurus and Stegosaurus, as well as carnivores such as Ceratosaurus and Torvosaurus.
Story
In the early 1990s, InGen had completed 12% of the Allosaurus genome for exhibition in the original Jurassic Park on Isla Nublar, but this completion of its DNA sequencing had to be put on hold due to InGen’s financial trouble. The sequencing of its DNA would eventually be finished by the time that Jurassic World opened up to the public.
The Allosaurus toy from the Jurassic Park 3D toy line (see the «Toys» tab for images) is one of the many dinosaur toys seen inside a toy store in the Main Street of Jurassic World.
Allosaurus is one of the dinosaurs in the Holoscape inside the Innovation Center of Jurassic World.
Jurassic World: Fallen Kingdom
Allosaurus roaring at Gyrosphere in Jurassic World: Fallen Kingdom
It is revealed that there are surviving Allosaurus populations remaining on Isla Nublar after the 2015 Incident, but will now face an impending danger, alongside many other creatures, in the form of an erupting volcano.
Interestingly, unlike the rest of InGen’s cloned theropods, the wrists of the adult Allosaurus are not pronated, though juveniles do have pronated wrists. It has a thicker head than in real life, and it was slightly oversized, being 10.4 meters (34 feet) instead of 9.7 meters (32 feet). Adults have exaggerated crests and spines running down their backs. The Allosaurus clones as adults are mostly dark greyish blue with a yellow underbelly, and a blue tongue while the juveniles are mostly dark blueish-grey with yellow underbellies, yellow stripes on the face and neck, a yellow circle around its eye orbit, white markings, and faded red on their crests.
The Allosaurus is introduced during the stampede, where one runs up to a Gyrosphere with Claire Dearing and Franklin Webb in it and gets tripped and killed by a falling magma rock from Mount Sibo.
Allosaurus in the cage room in Jurassic World: Fallen Kingdom
At least five other Allosaurus are later captured by Ken Wheatley and his men and are taken off of the doomed island to Lockwood Manor, where they are auctioned off to the highest bidder by Eli Mills and Gunnar Eversol. During the auction, a juvenile is bought by a wealthy client. The remaining Allosaurus are later seen running free in a stampede with other dinosaurs to escape the estate, while the juvenile that was bought at the auction is last seen in a truck being shipped off to its buyer.
Battle at Big Rock
- «Allosaurus. Definitely a carnivore.»
- —Kadasha(src)
The Allosaurus roaring at an adult Nasutoceratops and her young
One year after the dinosaurs’ escape from Lockwood Manor, one of the juvenile Allosaurus has fully matured and taken up residence in Big Rock National Park. It attacked a family of Nasutoceratops that were foraging at a camping ground, only to turn its interest on a family of campers in an RV. The Allosaurus destroyed the RV, but was scared off when Kadasha fired two crossbow bolts into its face.
Описание
реконструкция аллозавра (MOR 693)
Аллозавр был типичным крупным тероподом, передвигающимся на двух задних ногах, он имел массивный череп на короткой шее, длинный хвост и уменьшенные передние конечности. Передние и задние конечности имели по три развитых пальца, заканчивающихся крупными когтями.
Череп
Массивный череп достигал длины 845 мм, каждая предчелюстная кость (левая и правая) на кончике рыла содержала пять зубов D-образного поперечного сечения, верхняя и нижняя челюсти содержала от 14 до 17 зубов на каждой стороне. Зубы становились короче и более изогнутыми к задней части черепа, у всех зубов были пилообразные, зубчатые края, после утраты зубы заменялись новыми.
Большой Ал II (SMA 0005)
Череп имел пару надбровных гребней над глазами, состоящих из расширений слезных костей, различавшихся по форме и размеру. Гребни, вероятно, были покрыты кератиновой оболочкой и могли выполнять различные функции, в том числе выступать в качестве защиты для глаз, использоваться для демонстрации или использоваться в бою с другими представителей того же вида, хотя это очень маловероятно. Интересно, что вдоль верхних краёв носовых костей тоже шли гребни, приходящие к рогам, а на задней стороне черепной крышки находился гребень для поддержания мышц, как у тираннозаврид.
Слёзные кости имели небольшие углубления, в которых содержались железы. Внутри максиллы находились развитые синусы, связанные, судя по всему, с обонянием и вомером, игравшим значительную роль в социальном поведении. Крышка мозговой коробки была тонкой, что обеспечивало улучшенную терморегуляции мозга. Череп и нижняя челюсть имели особые суставы: они позволяли задним и передним костям челюстей свободно двигаться, увеличивая таким образом укус животного.
Посткраниальный скелет
Позвоночник состоял из девяти шейных, четырнадцати спинных и пяти крестцовых позвонков. Хвост аллозавра уникален у каждой особи и насчитывает от 45 (по словам Грегори Пола) до 50 позвонков (по мнению Джеймса Мэдсена). Шейные и переднеспинные позвонки имели полости для поддержания воздушных мешков, уменьшавших вес аллозавра. Подобные мешки встречаются в более поздних тероподов и птиц. Также они были одним из средств дыхания. Грудная клетка была широкой, придавая груди бочкообразную форму. Это отличает аллозавра от менее производных тероподов. Гастралия (брюшные рёбра) аллозавра известна по частичным находкам, видимо, плохо окостеневала. Есть один образец с прижизненными травмами. У аллозавра была птичья кость — вилочка, однако её наличие было признано только в 1996 году. До этого её иногда путали с гастралией.
Подвздошная кость массивная, лобок имел выступающий отросток, служащий для прикрепления мышц.
Систематика
Реконструкция подростка аллозавра
Аллозавр входит в семейство аллозавриды — одно из четырёх семейств карнозавров. Кроме аллозавров туда входят синрапториды, кархародонтозавриды и неовенаториды. В некоторых источниках аллозаврид делают предками тираннозавров (как это было в книге Грегори Пола «Хищные динозавры мира»), хотя они относятся к разным инфраотрядам, а ближайшей группой к аллозаврам являются кархарадонтозавриды. Всего к аллозавридам можно с уверенностью отнести три рода — аллозавра, заурофаганакса и французского аллозаврида без описания. Есть также вероятность, что такие ящеры как эпантериас и антодромей являются самостоятельными родами аллозаврид, но они могут быть и синонимами аллозавра.
Анализ 2010 года:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Description
The Ankylosaurus is the largest species of ankylosaurid dinosaur, which originated in North America during the Late Cretaceous period. The base genome of the Ankylosaurus bred by InGen for Jurassic World are a dull greyish-brown color.
Ankylosaurus is one of the most well-defended herbivores thanks to its thick armor and powerful bone-breaking club tail. This is in contrast with its short lifespan and low immunity to diseases. Its moderate cost and space requirements offset this, making it is less expensive to modify its genes to increase its immunity and lifespan.
Behavior
Preferring to be enclosed with smaller numbers of dinosaurs, the Ankylosaurus is one of the least social herbivores in the game, as it tolerates no more than four individuals of its species. While it can be kept with small carnivores such as Velociraptor and Dilophosaurus, it will fight with large carnivores or other herbivores if the enclosure gets overcrowded.
Виды
-
DINO 11541 в куске породы
Allosaurus fragilis (Marsh, 1877) — типовой вид (неотип USNM 4734), описанный Маршем. Датируется киммериджем-титоном. Обитал на территории Колорадо, Монтаны, Нью-Мексико, Оклахомы, Юты, Южной Дакоты и Вайоминга. Раньше его конечности использовали для определения новых видов.
- Allosaurus europaeus (Mateus et al., 2006), описан по неполному черепу (ML 415) из Португалии. Первоначально был определён как A. fragilis, но отличается от него строение черепа. Европейский вид датируется более ранним ярусом юрского периода.
- Allosaurus jimmadseni (Chure & Loewen, 2020) — голотип DINO 11541, обитавший на территории Юты. Отличается от типового вида строением черепа. Обитал по соседству с ним, возможны даже межвидовые стычки и конкуренция.
Синонимы
Почти все синонимы относятся к A. fragilis, за некоторым исключением.
- Antrodemus Leidy, 1870 — аллозаврид, описанный на основе неполных позвонков. Очень фрагментарен, поэтому может рассматриваться как синоним аллозавра.
- Creosaurus Marsh, 1878 — изначальное название A. atrox.
- Epanterias Cope, 1878
- A. atrox Marsh, 1878 — считался самостоятельным видом.
- A. amplus Marsh, 1879
- A. whitei — неофициальное наименование для двух полных скелетов A. atrox.
- Labrosaurus Marsh, 1879 — некогда считался самостоятельным родом на основе необычного зазора в заднем конце зубного ряда и расширенной, повернутой назад задней части нижней челюсти. Позднее эти отличия были приняты следствием паталогии.
- Madsenius Bakker, 1990(nomen nudum) — название было предложено Ламбертом в 1990 для останков из национального парка динозавров, приписываемых аллозавру или креозавру. Их описал Боб Баккер, однако сейчас мадсений считается очередным синонимом аллозавра, так как его выделили из-за отличий, появившихся вследствие неправильной реконструкции Гилмора.
- Allosaurus maximus Chure, 1995 — выделен в собственный род Saurophaganax
- Wyomingraptor Bakker, 1997(nomen nundum) — название, придуманное Робертом Баккером для нескольких образцов аллозавра, хранящихся в Геологическом музее Тейта. Не был описан официально.
- «Camptonotus» amplus Marsh, 1878
- Allosaurus lucasi (Dalman, 2014) — два частичных скелета, принадлежащих взрослому и несовершеннолетнему из Каньона МакЭлмо в округе Монтесума, на юго-западе Колорадо, которые были обнаруженный в 1953 году.
- «Allosaurus agilis» — результат опечатки.
- «Allosaurus ferox» — результат опечатки Марша, описывающего образец YPM 1893, относящийся к A. fragilis.
Description
Two Allosaurus fighting.
A ferocious apex predator and one of the world’s best-known dinosaurs, Allosaurus is one of the largest carnivores for Jurassic World operations on Isla Nublar and the Muertes Archipelago. The base genome of the Allosaurus is a blueish-grey body, a cream underbelly, light grey stripes covering its entire back, and a pair of red brow crests above its eyes.
Behavior
Allosaurus is a large, solitary theropod that doesn’t tolerate other large carnivores in their enclosure, even other Allosaurs, which can result in potentially fatal clashes. However, they can tolerate a decent number of other species in their enclosure, including small carnivores and herbivores. Allosaurus prefer large areas of open grassland to hunt in and prefer comparatively smaller areas of forest. The comfort threshold of the Allosaurus is high, comparable to Giganotosaurus, requiring powerful fences to be contained.
Систематика
Аллозавры относятся к семейству аллозаврид из надсемейства аллозавроид. Семейство аллозаврид было предложено в 1878 году Отниелом Чарльзом Маршем, но этот термин не употреблялся до 1970-х годов, а всех аллозавроид и карнозавров относили в одно семейство мегалозаврид.
После публикации трудов Мадсена об аллозаврах, термин «аллозавриды» стал использоваться многими палеонтологами. Как показывают исследования, представители семейства аллозаврид обычно были крупнее мегалозаврид. Очень близки к аллозавридам такие динозавры, как индозавр, пятницкизавр, Piveteausaurus, янхуанозавр, акрокантозавр, Chilantaisaurus, Compsosuchus и Szechuanosaurus.
Аллозавриды были одним из семейств надсемейства аллозавроидов, к которому также относятся кархародонтозавриды и синрапториды. Ранее именно аллозавроиды считались предками тираннозаврид, и их родственниками считались такие динозавры, как Stokesosaurus, но сейчас установлено, что это не так.
В культуре
- Аллозавр появляется в фильме 1925 года «Затерянный мир».
- В 1999 году аллозавр участвует в сериале BBC «Прогулки с динозаврами».
- В юрском сегменте документального фильма Discovery «Когда по Америке бродили динозавры» аллозавр назван самым совершенным хищником своего времени — позднего юрского периода. Сначала он предпринимает неудачную атаку на подростка-апатозавра, затем убивает цератозавра. Когда один из апатозавров падает и не может подняться, несколько аллозавров бросаются на него и добивают.
- В 2005 году аллозавр появился в фильме «И грянул гром».
- В 2018 году Аллозавр был показан в «Мир юрского периода 2».
- Аллозавра показали в документальном фильме «Планета динозавров».
- Аллозавр появляется в игре Jurassic World: The Game.
- Аллозавр появляется в компьютерной игре «ARK: Survival Evolved», где представлен стайным хищником, получающим бонус в стае.
Information Edit
The forelimbs of Allosaurus were short in comparison to the hindlimbs (only about 35% the length of the hindlimbs in adults) and had three fingers per hand, tipped with large, strongly curved and pointed claws. The arms were powerful, and the forearm was somewhat shorter than the upper arm (1:1.2 ulna/humerus ratio). The wrist had a version of the semilunate carpal also found in more derived theropods like maniraptorans. Of the three fingers, the innermost (or thumb) was the largest, and diverged from the others. The phalangeal formula is 2-3-4-0-0, meaning that the innermost finger (phalange) has two bones, the next has three, and the third finger has four. The legs were not as long or suited for speed as those of tyrannosaurids, and the claws of the toes were less developed and more hoof-like than those of earlier theropods. Each foot had three weight-bearing toes and an inner dewclaw, which Madsen suggested could have been used for grasping in juveniles.There was also what is interpreted as the splint-like remnant of a fifth (outermost) metatarsal, perhaps used as a lever between the Achilles tendon and foot.
In 1991 «Big Al» (MOR 693), a 95% complete, partially articulated specimen of Allosaurus was discovered. It measured about 8 meters in length. MOR 693 was excavated near Shell, Wyoming, by a joint Museum of the Rockies and University of Wyoming Geological Museum team. This skeleton was discovered by a Swiss team, led by Kirby Siber. The completeness, preservation, and scientific importance of this skeleton gave «Big Al» its name; the individual itself was below the average size for Allosaurus fragilis, and was a subadult estimated at only 87% grown. The specimen was described by Breithaupt in 1996. Nineteen of its bones were broken or showed signs of infection, which may have contributed to «Big Al’s» death. Pathologic bones included five ribs, five vertebrae, and four bones of the feet; several damaged bones showed osteomyelitis, a bone infection. A particular problem for the living animal was infection and trauma to the right foot that probably affected movement and may have also predisposed the other foot to injury because of a change in gait. Al had an infection on the first phalanx on the third toe that was afflicted by an involucrum. The infection was long lived, perhaps up to 6 months.
It is known that Allosaurus led a dangerous life. The Allosaurus on display at the Smithsonian Institute has a smashed shoulder blade, many broken ribs, and a lower jaw so damaged that paleontologists didn’t realize it was an Allosaurus jaw for over 100 years. But these were tough dinosaurs: Their bones show that they lived long enough for their wounds to heal.
Allosaurus had extensions on its lacrimal bones which formed a brow horn over each eye. These horns varied somewhat in shape and size. Low ridges extended from them along nasal bones. Some theories on the purpose of the horns include display, weapons for combat, and possibly as effective sunshades. These horns, likely covered in keratin, are believed to have been fragile.
Allosaurus probably spent time lurking in the undergrowth waiting for an unsuspecting herbivore to pass by. They may have also hunt in packs, preying on the stragglers in a large herd of herbivores, like the young, old, and wounded. Allosaurus may have used hunting strategies such as flesh grazing, pack hunting, and ambush attacks that utilized trachea crushing bites. It likely grasped its meal with its legs and mouth and pulled its meal apart. Its unusual gaping jaw has spurred debate regarding Allosaurus using its head like a hatchet to attack and slice at prey.
CaracterísticasEditar
CráneoEditar
El cráneo del Allosaurus mide 1 m de largo y presenta numerosas aberturas que estaban unidas mediante refuerzos óseos. Gracias a esta particularidad se reducía el peso del cráneo a la vez que aumentaba su solidez. Además tenía unas protuberancias óseas sobre los ojos que en los machos era mayor y cambiaba de color en la época de celo. Su cráneo tenía una potencia de mordida bastante baja para un animal de su tamaño (360 kilogramos) y era incluso menor a la de un león (480 kilogramos), por lo que se cree que este animal no atacaba como el Tyrannosaurus, no atacaba a gran velocidad con la boca abierta e hincaba sus dientes con mucha fuerza en la carne de la presa, sino que este animal corría a gran velocidad y golpeaba con los dientes de la mandíbula superior, de una forma similar a la de los pájaros del terror. Tras esto desgarraba la presa con las garras de las patas traseras y arrancaba la carne con sus fuertes dientes (unos 70), que se reparaban de forma similar a la de los actuales reptiles.
Patas delanterasEditar
Las patas delanteras del Allosaurus eran bastante pequeñas y poseían tres dedos con garras. Este animal tenía las patas delanteras suficientemente grandes como para llegar a la mandíbula con ellas, sin embargo solía bajar el cráneo gracias a su cuello, que funcionaba como una grúa y arrancaba la carne con los dientes. También usaba los brazos para sujetar a la presa cuando la golpeaba con la mandíbula. También es posible que las usara para excavar en sus nidos para liberar a las crías, sus patas aparentemente inservibles podrían ser parte de su equilibrio, aparte de la cola.
Patas traserasEditar
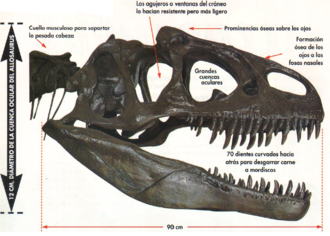
Cráneo de Allosaurus con los detalles anatómicos.
ColaEditar
Cuando se desplazaba, el Allosaurus mantenía erguida su larga y poderosa cola para mantener el equilibrio. La cola tenía unas 50 vértebras y resultaba muy útil para golpear a los posibles enemigos como dos machos en la época de celo o para eliminar a pequeños dinosaurios carnívoros como el Ornitholestes.
AlimentaciónEditar
Sus brazos tenían movimientos limitados, por lo tanto no eran tan útiles.
Probablemente en manadas se enfrentara a presas mas grandes, pero en solitario apenas podía enfrentar a animales cercanos a su tamaño, como jóvenes saurópodos o camptosaurus adultos que eran algo mas pequeños que él.
MaternidadEditar
Los bebés de Allosaurus nacían de unos huevos del tamaño aproximado de un balón de fútbol, que estaban enterrados en pequeños nidos similares a los de las avestruces. Al principio las crías, que al nacer medían unos 35 cm de largo, se alimentaban de insectos y partían sus exoesqueletos con sus pequeños y afilados dientes. A los pocos meses ya empezaban a comer carne y al cabo de un año su madre los abandonaba a su suerte. Las crías crecían bastante rápido y alcanzaban el tamaño adulto a los 12 años, tal como demuestran los abundantes fósiles del género. Los Allosaurus que no enfermaban podían llegar a vivir hasta 50 años.
En 1991 se encontró un esqueleto de Allosaurus perfectamente conservado. Pertenecía a un macho y tenía una gran cantidad de lesiones, lo que demuestra que el mundo de los dinosaurios era un lugar muy peligroso. Al espécimen se la apodó «Al» (una especie de diminutivo de Allosaurus) y vivió hace unos 145 millones de años, en lo que hoy es Wyoming.
In Real Life
Allosaurus was one of two apex predators of the Morrison Formation, the other being Torvosaurus. It could run anywhere between 30 to 55 kilometers per hour and likely preyed on ornithopods, stegosaurs, and other allosaurs. It is likely that Allosaurus itself was prey, as well; bite marks from other theropods, likely either Ceratosaurus or Torvosaurus, have been found on an Allosaurus pubic foot.
Allosaurus lived in a semiarid habitat that was dominated by large forests and open floodplains; an environment that was harsh and low on food. One notable bonebed, the Cleveland-Lloyd Dinosaur Quarry, is one of the most profitable sites to find Allosaurus remains; around 67% of all remains at the quarry are of allosaurs of various ages.
Allosaurus’ jaws had the widest gap of any known theropod, being capable of opening them to an angle between 79 and 92 degrees. It also had considerable control over its neck and head and could move the head quite rapidly. This is consistent with a feeding method similar to modern falcons, which pull back and up to remove flesh from a carcass.
The brain of Allosaurus was similar to that of a modern crocodile, which has implications about Allosaurus biology; the skull was held nearly horizontally, and it likely had an easy time hearing low-frequency sounds, although more subtle sounds were difficult for Allosaurus to hear.
While the largest specimens are 9.7 meters (32 feet) in length, most Allosaurus specimens measure about 8.5 meters (28 feet) long. Some fragments suggest it may have reached 13 meters (43ft) in length. Allosaurus was around 1,500 kilograms (3,300 pounds) on average, although large specimens may have weighed up to 2,500 kilograms (5,500 pounds).